Explain Where Potential Difference Occurs in an X Ray Circuit
A 45 cut makes the x-rays exit perpendicular to the axis of the tube. Up to 24 cash back Electrons strike target and produce X-rays ii A potential difference of 50 kV is applied across an X-ray tube.
An electron of kinetic energy 4 eV is fired in a direction parallel to the electric field through a tiny hole in plate A.
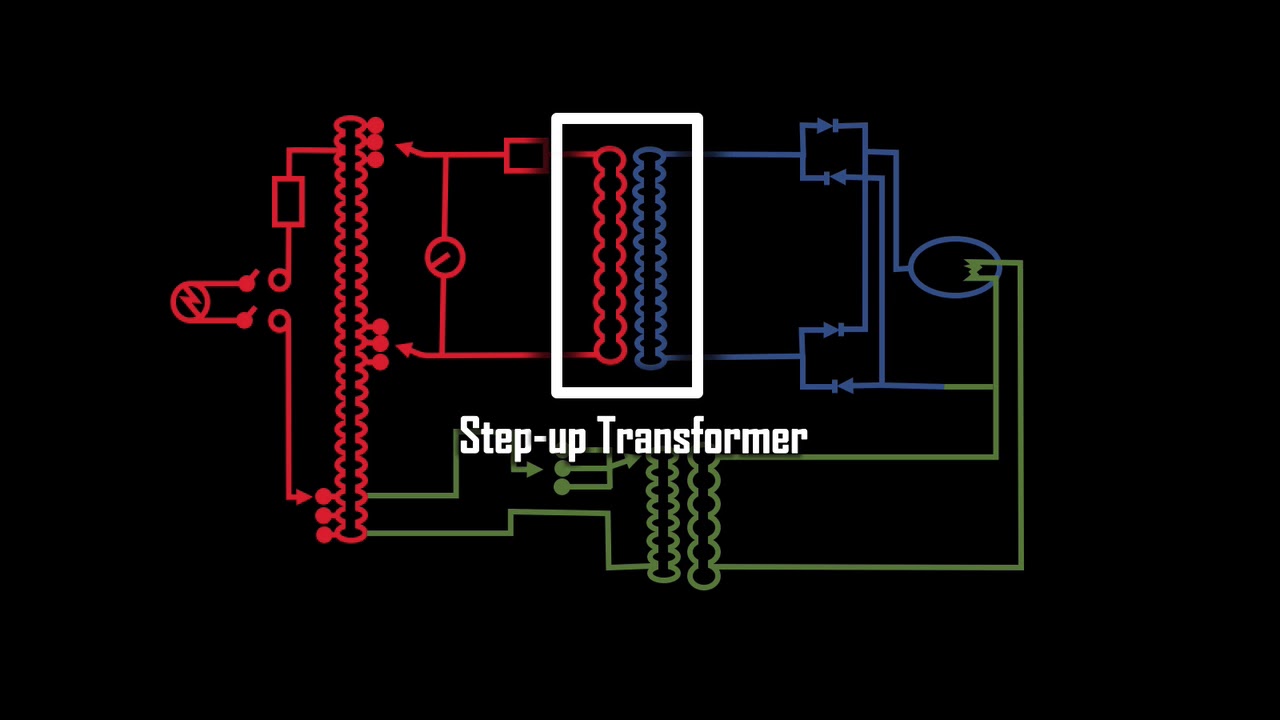
. The potential difference between points A and B that is the change in potential of a charge q moved from A to B is equal to the change in potential energy divided by the charge. Explain what is meant by an electric field. Electricity or current flows in the opposite direction of the flow of the electrons.
When a potential difference occurs in the conductor across two points the electrons get sufficient energy to flow from lower potency to higher potency in this conduction band against a small resistance offered by this conductor material. The tube has several design features to enable this to happen. If the electric potential difference between two locations is 3 volts then one coulomb of charge will gain 3 joules of potential energy when moved between those two locations.
They can be found in various forms such as in. A continuous and closed path of an electric current is called an electric circuit. The difference in charge between higher potential and lower potential is called a voltage or potential difference.
The potential difference between the plates is 6 V. The over usage of electricity in a circuit more than its limit is called. The highest power capacity is obtained by using three-phase power and high-speed rotation.
Low-energy X-rays are not useful in radiography but can deliver a significant dose. Which of the following is a correct expression for V. She is manipulating the field size by adjusting a device called the collimator which is attached to the x-ray tube housing.
At the end PE. The voltage or potential difference gives the force to the electrons to flow through the circuit. The filament circuit is the subcircuit of the main x-ray circuit shown as the lower portion of Fig.
6-2 BThis circuit is divided into two parts by the step-down transformer 11 and 12The primary purpose of the filament circuit is to supply a low current to heat the x-ray tube filament for thermionic emission of electrons. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. LatexDelta VfracDeltatextPEqlatex and ΔPE qΔV.
51 shows an X-ray tube. In other words X L X C. Radiographers can change the current and voltage settings on the X-ray machine in order to manipulate the properties of the X-ray beam produced.
B State how the resulting x -rays are affected by increasing the potential difference between the anode and the cathode. Thermal energy must be removed from the target. EV hf eV hc.
The quality and the quantity of the x-radiation are controlled by adjusting the electrical parameters kV tube voltage potential difference applied across the tube mA tube current flows through the tube and exposure. The picture you can see the technologist handling the x-ray tube. What is the function of a fuse during this situation.
An X-ray tube with its respective components placed in a vacuum and a generator make. The rectangular looking device just above the collimator is the housing for the x-ray tube. Series Resonance circuits are one of the most important circuits used electrical and electronic circuits.
Production of X-rays Module 9 Page 12. Assume that all the energy stored by the capacitor is used to heat up the bundle of wire. Different X-ray beam spectra are applied to different body parts.
States that the potential difference voltage across the total circuit or any part of that circuit is equal to the current amperes multiplied by the resistance ohms VIR Conductors materials with an abundance of free electrons that allow a relatively free flow of electricity. And finally if the electric. The potential difference between points A and B V B V A defined to be the change in potential energy of a charge q moved from A to B is equal to the change in potential energy divided by the charge Potential difference is commonly called voltage represented by the symbol ΔV.
A patient has an X-ray scan taken in hospital. However X-ray beams are typically filtered to minimize the low-energy component. X-rays are produced in an X-ray tube when fast moving electrons hit a.
5 The potential difference across a charged capacitor is V 0. Explain why the ratio of the. The high-energy X-ray photons interact with the.
All the photographs of x-ray tubes on this page have their targets aligned at this angle. The higher the voltage the greater the force and hence the more electrons flowing through the circuit. III Answer the following questions.
The diagram on the right shows the x-ray tube by itself. Target glass tube vacuum high speed electron beam X-rays copper rod black surface fins Fig. No external radioactive material is involved.
If the electric potential difference between two locations is 1 volt then one Coulomb of charge will gain 1 joule of potential energy when moved between those two locations. Simply understood the generation of X-rays occurs when electrons are accelerated under a potential difference and turned into electromagnetic radiation. What faults can occur with the x-ray tube.
Electrons must travel in one direction from Cathode to Anode so needs a POSITIVE POTENTIAL This will allows x-rays to be produced. Iii Most of the tube is surrounded by lead. 51 In the production of X-rays the target gets very hot.
And potential difference is the work done by moving a charge from one place to the another New questions in Physics calculate the value of the characteristic times for the tiny oildrop in the millikan oildrop experiment when its terminal speed 61x10-5 ms. The capacitor discharges through a fixed resistor. X-rays are produced within the X-ray machine also known as an X-ray tube.
A V V 0 2 B V V e 0 C V V 0 ln2 D V V e 0 ln Total for Question 5 1 mark. It is expanded in Fig. Potential difference is commonly called voltage represented by the symbol.
The potential difference across the capacitor is 12 V. Some x-ray tubes are cooled with water The target is cut on a diagonal so that the emitted x-rays fly off the surface at an angle different from the incident electrons. The point at which this occurs is called the Resonant Frequency point ƒ r of the circuit and as we are analysing a series RLC circuit this resonance frequency produces a Series Resonance.
After a time equal to the time constant the potential difference has reduced to V. A rating chart for an x-ray tube operated at different waveforms and rotation speeds is shown in the figure titled Rating Curves for an X-Ray Tube Operated under Different Conditions. Notice that the real advantage occurs at relatively short exposure times.
How does overloading and short-circuit occur in an electric circuit. Switch S 2 is now closed. Whenever the voltage is on a device can produce some X-rays even if the current is too low to read.
Start studying X-Ray Circuit Tube. Ii A high potential difference is applied between a cathode and the anode. I A potential difference is applied to the filament.
Calculate the increase in the temperature of the bundle of wire. A Explain why. Tungsten deposits reducing vacuum Glass may be.
At the beginning ½ mv el 2 eV olt v 13 108 m s1 iiiCalculate the minimum wavelength of the X-rays produced by the tube. Calculate the maximum velocity of an electron in the tube.
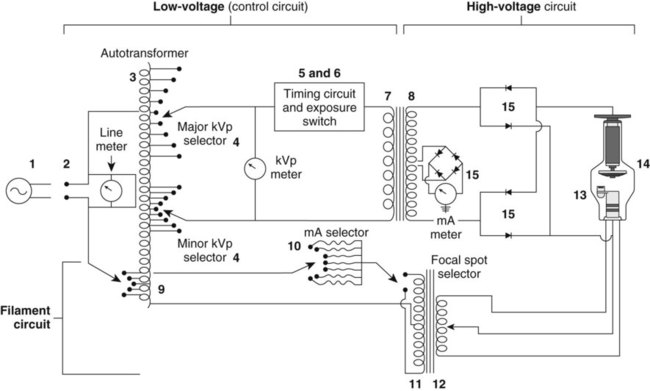
X Ray Circuit And Tube Heat Management Radiology Key

Comments
Post a Comment